What is polarisation of waves?
The phenomenon of restricting the oscillations of a wave to just one direction in the transverse plane is called polarisation of waves.
What is polarimeter?
Polarimeter is a device used for the measurement of optical rotation and the angle of rotation of the plane of polarisation rotated by an optically active substance.
What is plane of polarization and plane of vibration?
Plane of vibration: The plane containing the direction of vibration and the direction of wave propagation is called the plane of vibration.
Plane of polarisation: The plane passing through the direction of propagation and perpendicular to the plane of vibration is called the plane of polarisation.
What is Nicol prism and its function?
It is an optical device based on the phenomenon of double refraction which is used for producing and analysing plane polarised light. It consists of two pieces of calcite cut with a 68o angle and stuck together with Canada balsam.
What are o-rays and e-rays?
- The one ray which obeys the ordinary laws of refraction and has vibrations perpendicular to the plane of incidence is called O-ray or ordinary ray.
- The other ray which does not obey the laws of refraction and has vibrations parallel to the plane of incidence is called E-ray or extra-ordinary ray.
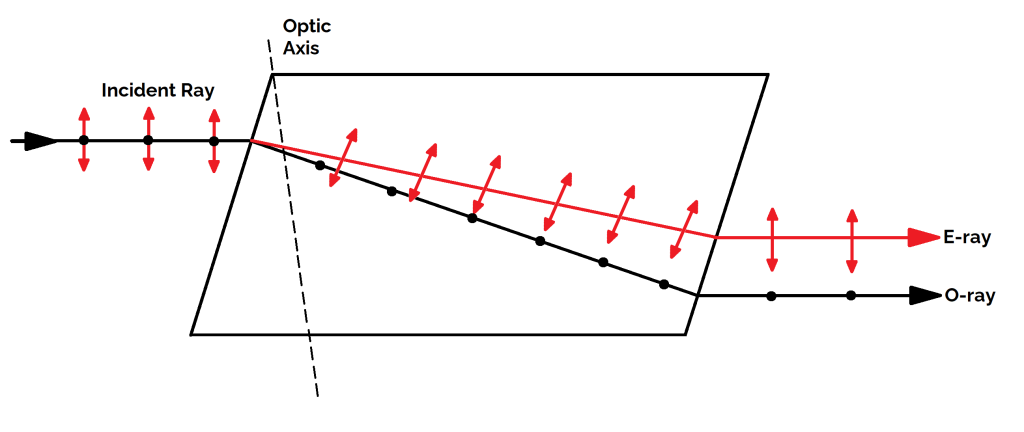
What is birefringent?
When an unpolarised ray passes through certain crystals like quartz or calcite, it splits up into two rays, as shown in the figure above. This phenomenon is called birefringence or double refraction.
Who follows Snell’s Law?
O-ray or ordinary ray obeys the ordinary laws of refraction and has vibrations perpendicular to the plane of incidence.
What is Specific Rotation? What is its unit?
The angle through which the plane of polarisation rotates when plane polarised light is passed through one decimetre length of solution containing one gram of the substance per cm3 .
Specific rotation can be defined as:
![]()
![]()
The unit of specific rotation is degrees per decimeter per gram per milliliter(or cm3)
What is Law of Malus?
This law states that when a beam of completely plane polarised light is passed through an analyser, the intensity ‘I’ of the transmitted light varies directly as the square of the cosine of the angle ‘θ’ between the transmission directions of polariser and analyser.
I=Iocos2 θ
where Io is the maximum intensity of transmitted light.
What is Brewester’s Law?
When unpolarized light is incident on a polarizing material at such an angle that the reflected light and refracted light are perpendicular to each other, the reflected light becomes completely polarized, and the refracted light is partially polarized. This is known as Brewester’s Law.
tan θB = µ
where θB= Brewster angle or angle of polarisation
What are positive and negative crystals?
Positive and negative crystals are types of birefringent materials where light splits into ordinary and extraordinary rays. In a positive crystal like quartz, the extraordinary ray travels slower, i.e., it has a higher refractive index. In a negative crystal like calcite, the extraordinary ray travels faster and thus has a lower refractive index.
What are dextrorotatory and levorotatory substances? Give an example.
Dextrorotatory substances rotate light to the right (clockwise). An example is sucrose.
Levorotatory substances rotate light to the left (counterclockwise). An example is cholesterol.
What is its least count? Give its unit.
The least count of a polarimeter is typically 0.1° and its unit is degrees.